What is flute lamination?
Flute lamination refers to the process of bonding additional layers of material to a corrugated substrate to enhance its functional or aesthetic properties. Here's a detailed breakdown:

Core Components and Process:
Fluted Substrate: The core component is typically corrugated material, which consists of a wavy, fluted layer sandwiched between flat linerboards. This structure provides rigidity, cushioning, and lightweight strength.
Lamination: A thin layer of material is applied to one or both sides of the fluted substrate. This is done using heat, pressure, or adhesives.
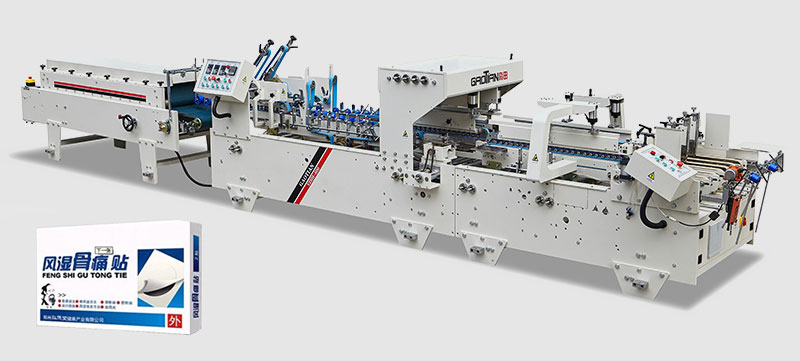
Lamination Machinery:
Semi-automatic corrugator can combine different paper layers to connect to corrugated paper. It utilizes a set of rollers and bonding mechanism to laminate the materials. This machine is suitable for small to medium production runs that need to strike a balance between cost and productivity. It helps to create strong paper composite materials that can be further processed into packaging products such as boxes and cartons, providing a practical solution for businesses.
Purpose:
Protection: Adds moisture resistance, UV protection, or chemical resistance.
Durability: Enhances tear resistance and structural integrity.
Aesthetics: Improves visual appeal with glossy/matte finishes or printed designs.
Functionality: Enables specific uses like food-grade safety, insulation, or static control.
Applications:
Packaging: Used in boxes for liquids, perishables, or high-end products.
Construction: Insulated panels or protective barriers.
Retail: Attractive displays or reusable packaging.
Flute lamination refers to a specialized manufacturing process primarily used in the packaging industry to create corrugated cardboard structures with enhanced strength and durability. This technique involves bonding together multiple layers of paper or cardboard, one layer features a corrugated design that provides rigidity and cushioning, while the other layers act as protective liners.